Radar Meteorology Glossary
This glossary will be the main reference for radar products and problems and will give details on what the different products are and how they are used.
Browse the glossary using this index
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
S |
|---|
S-Band RadarA 10 centimetre wavelength radar. | |
Sample volumeThe volume in which the radar data for one range bin are measured. Defined by the width of the radar beam (app. 1°) and half the length of the transmitted pulse. 1 µs pulses are 150 m deep, 2 µs pulses are 300 m deep. | ||
SaturationUpper limit of dynamic range above which an increase in the input signal produces no detectable change in the output. | |
Scanning StrategyA volume scanning procedure designed for the surveillance of one or more particular meteorological phenomena. | |
Sea clutterSea clutter is a specific form of spurious echo feature. The main reason of its formation is anomalous propagation of partial radar beam above water bodies, i.e. ducting. Sea clutter can be treated by identifying multiple modes of the reflictivity spectrum and then treating each mode differently. Example Image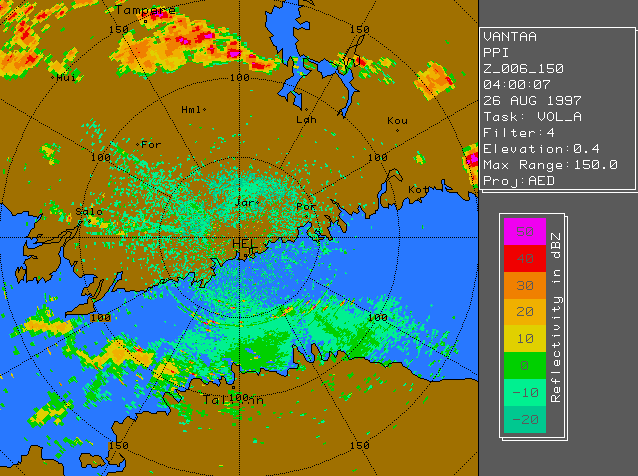 | ||
Ships in radar imagesProblems caused in radar productsDoppler filter is useless when sidelobes hit the ship because of the movement of the ship. Ships and their sidelobe echos can be detected and removed using pattern recognition methods to polar data.Example Image | |
Side LobeSecondary energy maximum located outside the radar beam. Typically contains a small percentage of energy compared to the main lobe. | |
Sidelobe echoProblems caused in radar productsSecondary maxima of radar beam is called sidelobes. Echos caused by sidelobes are seen in wrong directions. Typically sidelobes are much weaker than the main one. So the problem exist if only it is very strong echo (hail, ship, ground clutter).Example Image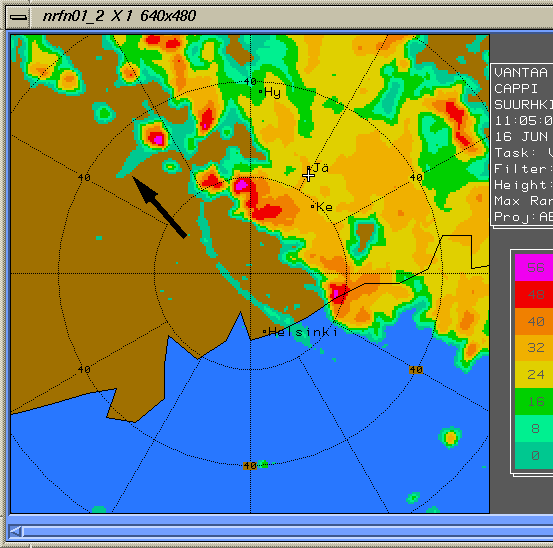 | |
Specific differential phase shiftDescriptionThe Specific Differential Phase KDP denotes the difference between the propagation constant for the horizontally and vertically polarized wave. In a homogeneous medium KDP can be directly obtained from the differential phase shift φDP at two different locations. Notes• KDP is only affected by anisotropic hydrometeors (rain) and therefore KDP allows to discriminate between rain and frozen precipitation. | ||