Radar Meteorology Glossary
This glossary will be the main reference for radar products and problems and will give details on what the different products are and how they are used.
Browse the glossary using this index
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
K |
|---|
Kalman FilterA linear system in which the mean squared error between the desired output and the actual output is minimized when the input is a random signal generated by white noise. | |
KlystronAn electron tube used as a low power oscillator or a high power amplifier at ultrahigh frequencies. Used for exceptional stability over long periods of transmission. | |
L |
|---|
Layer Mean ReflectivityThe layer mean reflectivity is a 2D-map showing the mean reflectivity in a user-defined layer between two CAPPI surfaces. | |
Layer turbulenceDescription2D map containing the mean spectral width between set upper and lower limits in altitude in the vertical column over each surface point (ground view) LTB is calculated using a polar volume data set with spectral width as input. ParametersRange: diplayed rangeImage size Pixel resolution Top: Height above MSL of upper data layer Bottom: Height above MSL of lower data layer NotesLTB can be used to observe turbulence on flight levels. The radar scan should be optimized for this purpose, low antenna rotation speed to get a good enough data set of W. | ||
Linear depolarisation ratioDescriptionThe linear depolarization ratio LDR is the ratio of the vertically polarized reflectivity to the horizontally polarized reflectivity for a horizontally polarized transmitter pulse, in other words: the ratio of the cross-polarized reflectivity to the co-polarized reflectivity. Notes• Measurement needs usually different radar measurement mode. | ||
M |
|---|
MagnetronAn electron tube used as a high power oscillator in the microwave bands. This produces pulse to pulse variations that make it unstable for Doppler radar use. | |
Main lobeThe envelop of electromagnetic energy along the main axis of the beam. | |
Maximum Unambiguous RangeThe greatest distance a pulse can travel and return before the next pulse is transmitted. Ru = C / (2*PRF) | |
Maximum vertical reflectivityDescription2D map containing the maximum reflectivity present in the vertical column over each surface point (ground view). In addition and optionally, the maximum reflectivity taken along a set of horizontal planes at different altitudes and along specified directions can be given (side-walls). Notes• It is assumed that the level slicing used for the side-walls intensity is the same than for the ground map.• For side-walls, if the height increment is constant then the vertical spacing is given instead of specifying the sequence of height values. • If side-walls are present, then their number, orientation and height sequence are omitted. Example image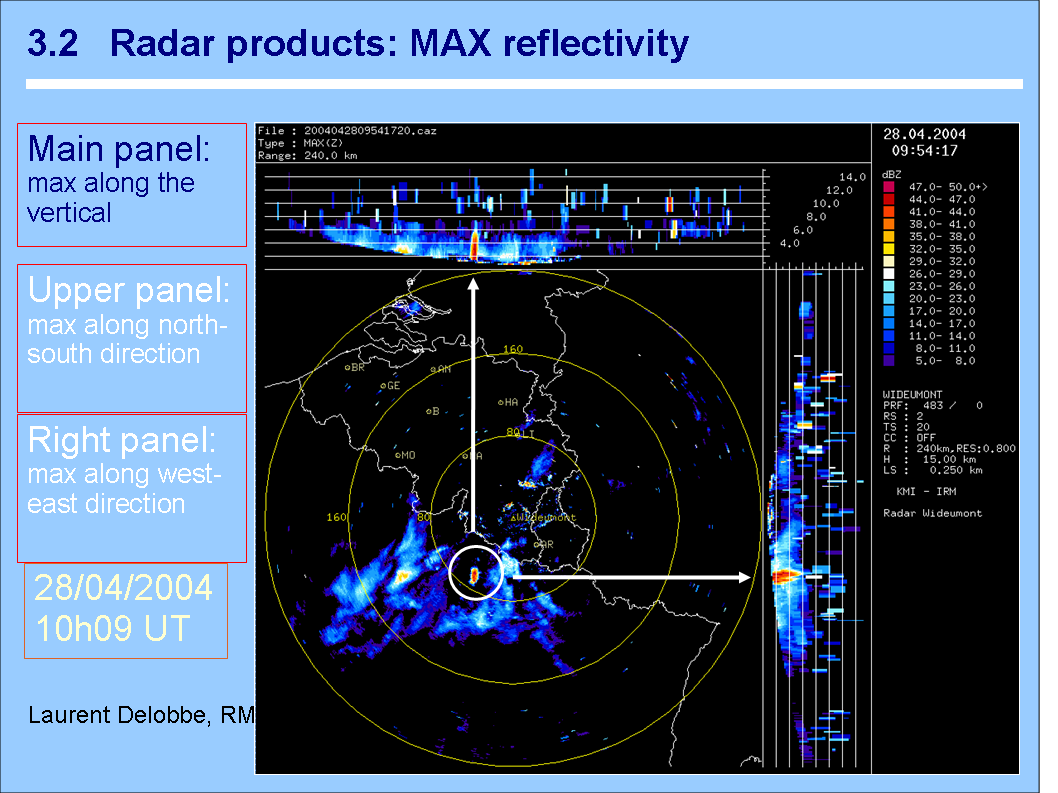 | |