Radar Meteorology Glossary
This glossary will be the main reference for radar products and problems and will give details on what the different products are and how they are used.
Browse the glossary using this index
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
M |
|---|
Mean Doppler VelocityReflectivity weighted average velocity of targets in a given volume sampled. Usually determined from a large number of successive pulses. Also called mean radial velocity. | |
Minimum Discernable SignalA.K.A: MDS. In a receiver, the smallest input signal that will produce a detectable signal at the output. This value is a measure of receiver sensitivity. | |
MiscalibrationMiscalibration influences compositing and produces biases in the rainfall rate estimates. It is difficult to correct precipitation attenuation because of it. An overestimate of Z produces an exponentially increasing error. Example Image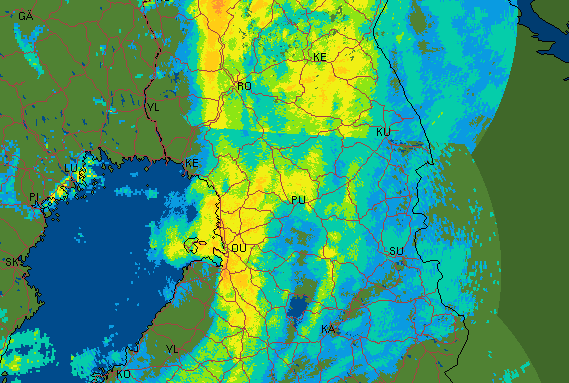 | |
Monostatic RadarA radar system in which the same antenna is used for transmission and reception of energy. | |
Multiple Trip EchoesSignal returns from a pulse other than the most recent. See also Range Folding. | |
N |
|---|
Nyquist VelocityWhen the radial component of target velocity exceeds one half wavelength (or 180 degrees) the measurement of the phase change between transmitted and received pulses is ambiguous. This results in radial velocity which is aliased. The velocity at which this occurs is the Nyquist Velocity. VN = PRF*λ/4 | |
O |
|---|
Operational ModeA combination of scanning strategies and product mixes tailored to one or more meteorological situations. | |
Orographic enhancementThe precipitation process can be enhanced by the seeder-feeder mechanism. Convective cells aloft can produce large precipitation particles, falling through a lower cloud layer and growing at the expense of the water content at the lower cloud. | |
Overhanging emittersRadar pictures get infected by microwaves coming from other radars and microwave links. Most of the emitters can be discovered by pattern recognition from polar data. Example Image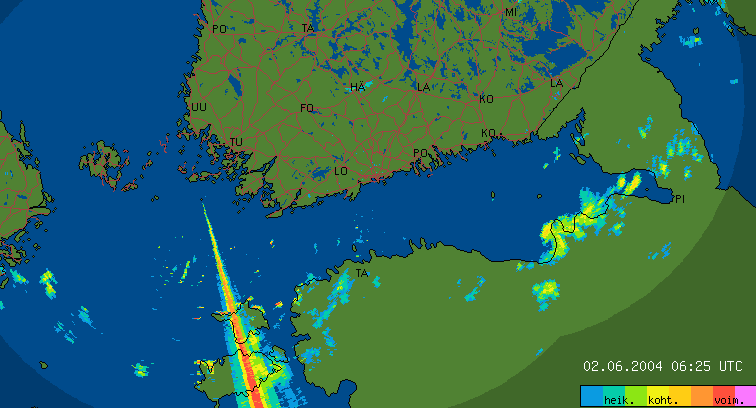 | ||