Radar Meteorology Glossary
This glossary will be the main reference for radar products and problems and will give details on what the different products are and how they are used.
Browse the glossary using this index
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
A |
|---|
A ScopeA cathode ray tube that uses amplitude modulated signals to display signal strength versus target range. Also known as the A-Indicator or the A/R scope. | |
AbsorptionThe retention of incident radiation by an intercepting substance. | |
AliasingAmbiguous detection in a sample data system. Aliasing occurs when the input frequency exceeds one half the sampling frequency. See also Velocity Aliasing. In radar, the folding of target returns from outside the normal unambiguous range interval (range folding) into the normal range interval, or the folding of radial velocity measurements outside the unambiguous velocity interval (velocity folding) into the normal velocity interval. | |
Aliasing ThresholdThe maximum radial velocity which a Doppler radar can unambiguously detect. See also Velocity Aliasing, Nyquist Velocity. | |
Anomalous Propagation ClutterAnomalious propagation (AP) is a mirage on a radar. Ground clutter, high superrefraction, echos beyond maximum unumbiguous range and biometeors, mountains are common AP signatures. If there are data from more than one radar, AP and false echos are easy to identify, because the neighboring radars generally won't see the same thing. If only one radar is available, it is possible to look at different elevation angles and it can be found that AP tends to be confined to the lowest elevation angles. Example Image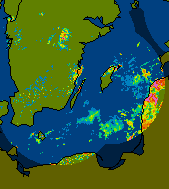 | ||
Antenna GainThe measure of effectiveness of a directional antenna as compared to an isotropic radiator, maximum value is called antenna gain by convention. | |
Antenna pointing errorAntenna of pointing error in elevation affects the H of the measurements which is in turn important for the vertical profile correction. The effect is significant at low elevations. Regular technical service of the antenna s essential to decrease antenna pointing problem. | |
AsymptoticThe condition where a line is a limit to one or more curves at an infinite distance from the origin. | |
Attenuation by precipitationThe equation dBZc = dBZ + 2CrΣ(ZE) is used for getting corrected values of attenuation by precipitation. Example Image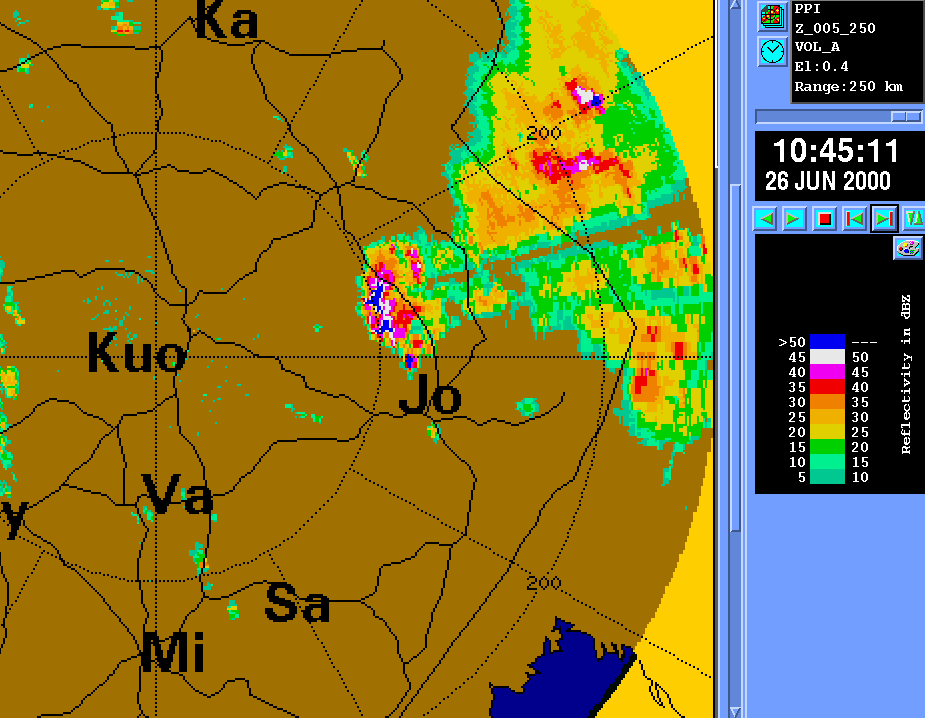 | ||
AutocorrelationA measure of similarity between delayed and undelayed (time, space, etc) versions of the same function. | |