Radar Meteorology Glossary
This glossary will be the main reference for radar products and problems and will give details on what the different products are and how they are used.
Browse the glossary using this index
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
M |
|---|
MagnetronAn electron tube used as a high power oscillator in the microwave bands. This produces pulse to pulse variations that make it unstable for Doppler radar use. | |
Main lobeThe envelop of electromagnetic energy along the main axis of the beam. | |
Maximum Unambiguous RangeThe greatest distance a pulse can travel and return before the next pulse is transmitted. Ru = C / (2*PRF) | |
Maximum vertical reflectivityDescription2D map containing the maximum reflectivity present in the vertical column over each surface point (ground view). In addition and optionally, the maximum reflectivity taken along a set of horizontal planes at different altitudes and along specified directions can be given (side-walls). Notes• It is assumed that the level slicing used for the side-walls intensity is the same than for the ground map.• For side-walls, if the height increment is constant then the vertical spacing is given instead of specifying the sequence of height values. • If side-walls are present, then their number, orientation and height sequence are omitted. Example image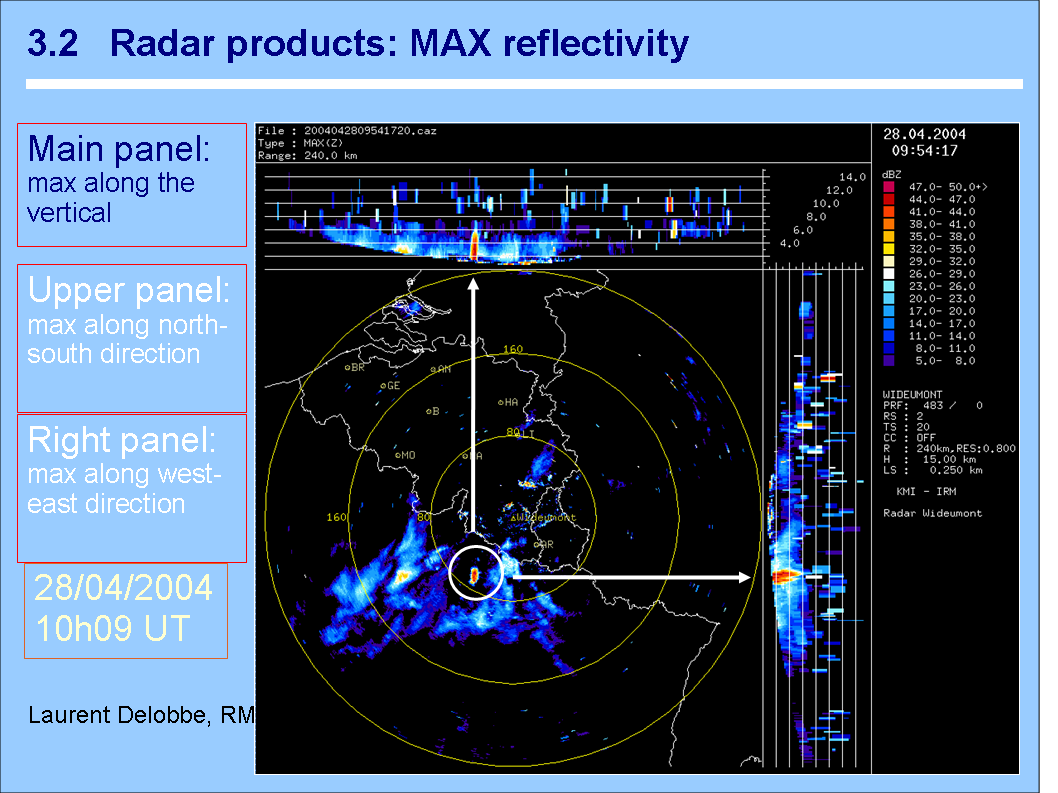 | |
Mean Doppler VelocityReflectivity weighted average velocity of targets in a given volume sampled. Usually determined from a large number of successive pulses. Also called mean radial velocity. | |
Minimum Discernable SignalA.K.A: MDS. In a receiver, the smallest input signal that will produce a detectable signal at the output. This value is a measure of receiver sensitivity. | |
MiscalibrationMiscalibration influences compositing and produces biases in the rainfall rate estimates. It is difficult to correct precipitation attenuation because of it. An overestimate of Z produces an exponentially increasing error. Example Image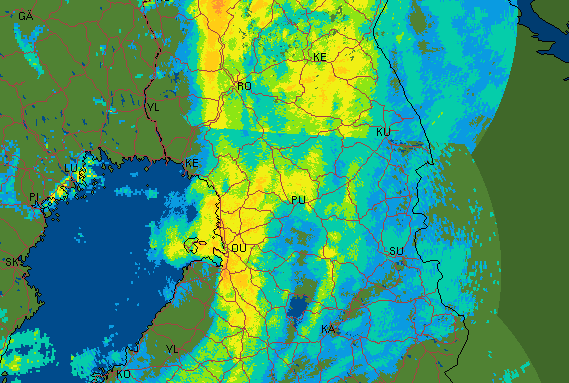 | |
Monostatic RadarA radar system in which the same antenna is used for transmission and reception of energy. | |
Multiple Trip EchoesSignal returns from a pulse other than the most recent. See also Range Folding. | |