Radar Meteorology Glossary
This glossary will be the main reference for radar products and problems and will give details on what the different products are and how they are used.
Browse the glossary using this index
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
W |
|---|
Weak Echo RegionWithin a convective echo a localized minimum of equivalent reflectivity, often associated with the strong updraft region. | |
Wet radome attenuationMicrowaves lose energy on a wet radome. Rain attenuation could be reduced by hydrophobic coating. The attenuation could be estimated by ground clutter echos, if target is not too far. Example Image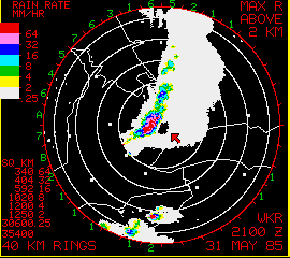 | ||
Wind shearDescription2D-map projection of a conical surface at predefined elevation containing change of the radial component of wind in Radial, Azimuthal or elevational direction or combined. ParametersProduct data quantity: wind shear in tenths of m/s/kmRadial, Azimuthal or elevation shear, or combined R+A, R+A+E, etc. Notes• The radial velocity data should be of high quality because of danger of false alarms. | ||
Wind speed and directionDescription2D-array of horizontal wind vectors, based on single Doppler radar measurements and eg. the uniform wind algorithm. ParametersProduct data quantity: array of speed (tenths of m/s and direction (degrees) of windImage size: number of arrays per row (# of columns) and per column (# of rows) Array spacing: km Upper limit altitude: m a.s.l. Lower limit altitude: m a.s.l. Range and Azimuth Spacing: These fields define the resolution of computing the wind vectors in polar coordinates. Quality indicator: Ref. WP 1.2 Notes• Because vertical shear can be substantial, it is recommended that the layer between upper and lower limit should be around 1 km• A quality indicator should be defined for this! | ||
WindmillsProblems caused to radar productsWindmills cause partial beam blockage. Beam blockage in turn causes a reduction in the quality of the surface precipitation estimates. The beam blockage can be estimated by considering the ratio of the intercepting area of the windmill and the local area of the radar beam. | |