Radar Beam Essentials
- Frequency ↔ wavelength
- PRF/PRT → Maximum unambiguous range, range folding
- Pulse length → range distortion, range resolution
- Beam width → azimuth distortion, azimuth resolution
- Sidelobes → ground clutter
Pulse Length And Spacing
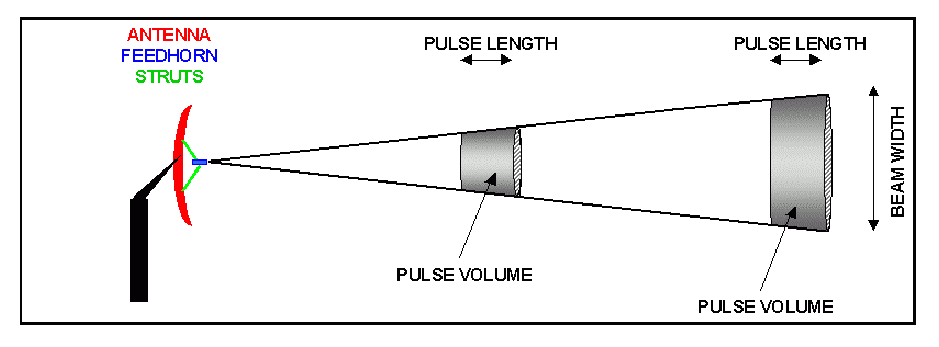
Definition of a pulse volume, pulse length and beamwidth. Note that the image is very exaggerated and in reality the beam is much more focused.
Beamwidth
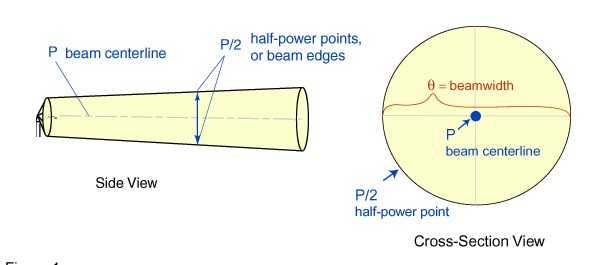
Radar beams have a finite angular width → Beamwidth

Definition of a Radar Beam width and maximum power line
-
Beamwidth ≈ wavelength / antenna diameter

The calculated Radar beam energy distribution as observed from the receiving end
The electromagnetic field transmitted by the radar is very focused along the center of the beam axis. The effect of diffraction of the electromagnetic field causes several auxiliary power maxima to occur, causing so-called sidelobes to the radar beam. Most of the power - about 80% - is radiated along the main beam, but some power is radiated through the sidelobes. It is generally ≥ 1000 times less intense (30 dB less).
The goal is to have a small beamwidth, and small sidelobes