Signal Processing
- Frequency domain = Fourier Transform techniques
- Time domain = Pulse Pair processing
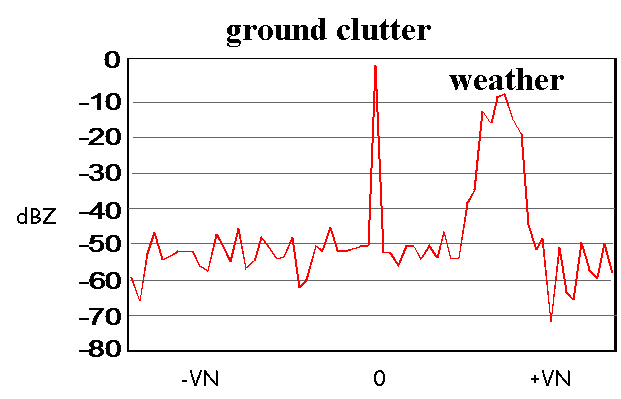
Signal Processing also involves filtering out of
- Ground clutter
- System noise
Pulse Pair processing is computationally less intensive than Fourier Transform techniques
Recall from physics, the Doppler frequency shift ...

There is a technical problem, with measuring small frequency shift (say 400 hz) on a 6 Ghz signal, within a 2 microsecond pulse: current technology cannot do it. Instead, we measure the change in phase from pulse to pulse.
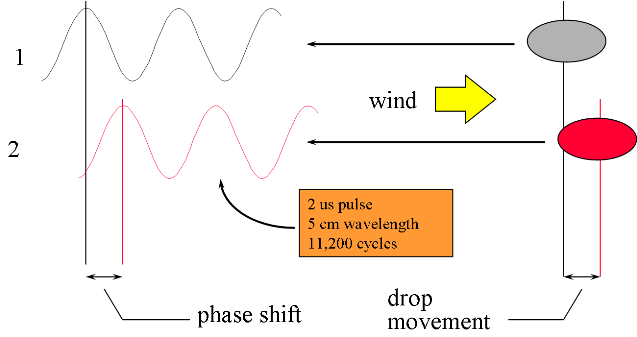

Figure 7.
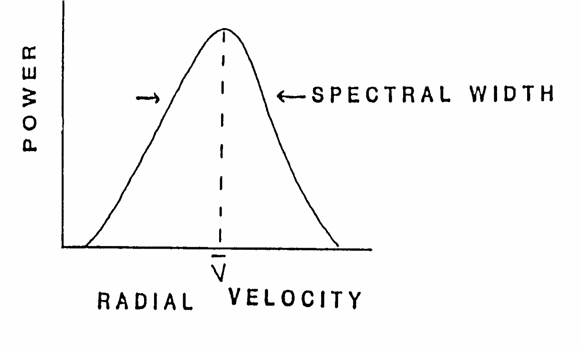
Doppler detects the phase change between the transmitted and received signal for each range bin. One pulse is not enough - several must be averaged to get reliable signal. A histogram of velocity measurements is assembled for each bin. The creation of a spectrum of velocities is done through the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). The mean velocity and spectral width can be calculated.
 |
|