Introduction
DEFINITION: POLARIZATION is the orientation of the electrical field component of an electromagnetic wave.
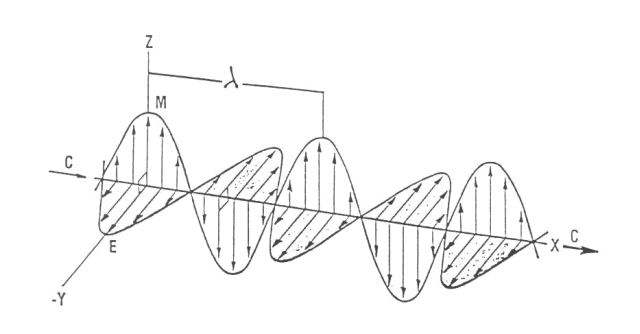
Figure 1. Electromagnetic energy characterized by linear horizontal polarization. Energy is propagating in the X direction at a speed equal to c. Wavelength of the electromagnetic energy (wave) is depicted.
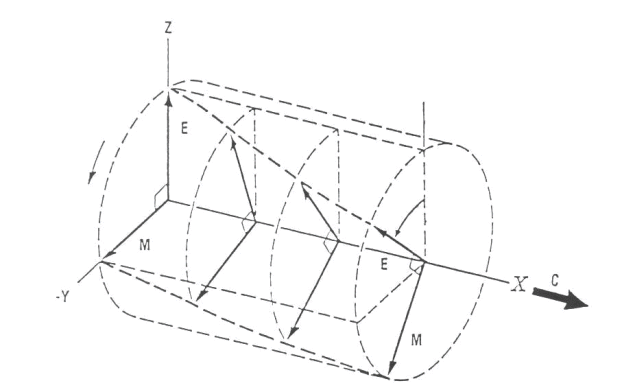
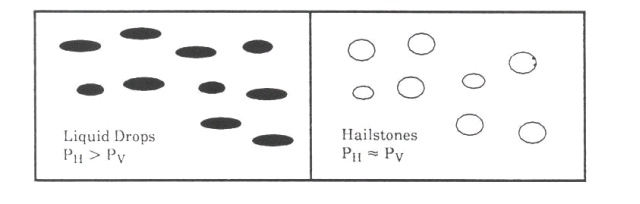
Polarization can also be circular. Circular polarization is characterized by an electrical field which rotates around the axis along which the electromagnetic energy is propagating. This rotation can be either to the right or to the left with respect to an observer situated at the origin of the electromagnetic energy (for example, the observer would be looking outbound along the azimuth of a radar). Right circular polarization is depicted in the figure above. Weather radars generally employ linear horizontal polarization. During its descent, liquid precipitation tends to assume the shape of an oblate spheroid (drops become aerodynamically flattened, with greater horizontal than vertical extent). The shape of the falling raindrop has dictated that radars used for precipitation detection be polarized in the horizontal to maximize the drop’s backscattered cross-section.
Air Traffic Control (ATC) radars are capable of employing either linear or circular polarization. Circular polarization is used to minimize the amount of power returned from precipitation so that aircraft locations may be more easily monitored. It is most successful in eliminating light liquid precipitation because the smaller drops tend to remain round rather than become oblate as they fall; therefore, if ATC radar operators wish to optimize aircraft detection, circular polarization should be employed. However, if precipitation detection is desired, linear polarization should be used.
Dual-polarized weather radar exist mainly in the research community, though they are starting to find their way into mainstream use. The Meteorological Service of Canada has a C-band dual-polarized radar at King City, Ontario, northwest of Toronto. McGill University in Montreal also has one, though it is an S-band version. These systems are capable of switching from linear horizontal to linear vertical polarization from one pulse to the next. Power returned from a given range gate in linear horizontal mode is compared to power returned from the same range gate in linear vertical mode. In regions of high reflectivity, the degree of variation in power returned may indicate whether or not hail is present.